
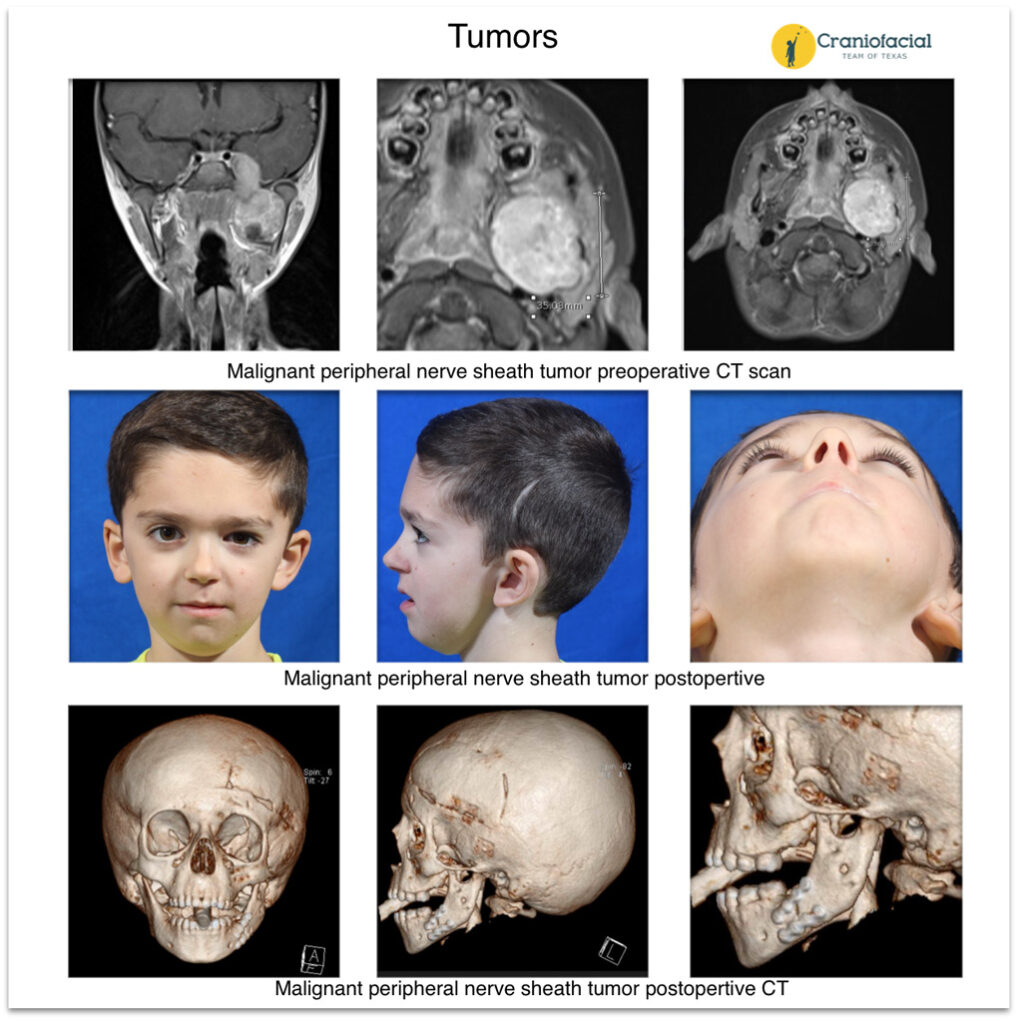
Head and neck cancer is a rare condition in children, but it can occur. The treatment options for head and neck cancer in pediatric patients are similar to those in adults and include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
When surgery is required, the procedure will depend on the location and stage of the cancer. Some of the common surgical procedures for head and neck cancer in pediatric patients include:
Excision: In this procedure, the surgeon removes the cancerous tissue and a margin of healthy tissue around it.
Lymph node dissection: This is a surgical procedure used to remove lymph nodes in the neck to check if the cancer has spread to these lymph nodes.
Endoscopic resection: This procedure is a minimally invasive technique used to remove cancerous tissue from the nose, throat, or other parts of the head and neck.
Glossectomy: This procedure involves removing part or all of the tongue to treat tongue cancer.
Laryngectomy: This procedure involves removing the voice box (larynx) to treat laryngeal cancer.
Maxillectomy or mandibulectomy: These procedures involve removing part or all of the upper or lower jawbone to treat maxillary or oral cavity cancer.
The goal of surgery in pediatric patients is to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible to reduce the risk of complications and to preserve the child’s normal function. It’s important to work with a pediatric head and neck surgeon with experience in treating pediatric patients to determine the best treatment plan for each individual case.

