

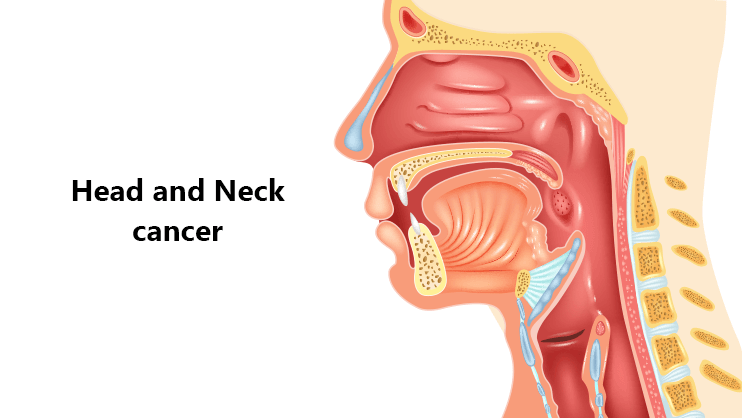
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that occur in the mouth, throat, larynx, nasal cavity, and salivary glands. These cancers often cause symptoms like persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, changes in voice, and lumps in the neck.
Screening for head and neck cancer may involve a physical exam, a review of medical history and risk factors, and imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI. Diagnosis typically involves a biopsy, in which a sample of tissue is removed and examined under a microscope.
Treatment options for head and neck cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Prevention measures for head and neck cancer include avoiding tobacco and alcohol use, practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of HPV infection, and wearing appropriate protective gear when working with certain chemicals and substances.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any persistent symptoms or signs of head and neck cancer. Early detection and treatment can improve outcomes and increase the chances of a successful recovery.
Here is some more information on Head and Neck Cancer:
Risk Factors: The most common risk factors for head and neck cancer include tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, exposure to certain chemicals and substances, and infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other factors that may increase the risk of developing head and neck cancer include age, gender (men are more likely to develop these cancers than women), and a weakened immune system.
Symptoms: The symptoms of head and neck cancer can vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. Some common symptoms include:
- Persistent sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Changes in voice, such as hoarseness or a raspy voice
- A lump or swelling in the neck
- Pain or difficulty chewing
- Ear pain or hearing loss
- Nosebleeds or a stuffy nose
- Persistent cough
Screening: Screening for head and neck cancer is not routine, but may be recommended for people who have an increased risk of developing the disease. The screening process may include a physical exam, a review of medical history and risk factors, and imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI.
Diagnosis: If head and neck cancer is suspected, the doctor may perform a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed and examined under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Other tests that may be used to diagnose head and neck cancer include imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI.
Treatment: Treatment for head and neck cancer may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. In some cases, a team of specialists may work together to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Recovery: The recovery process after treatment for head and neck cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the treatment approach used. Some people may experience side effects like fatigue, nausea, and difficulty swallowing, while others may experience long-term effects like difficulty speaking or eating. It’s important to follow up with your doctor regularly after treatment to monitor for any signs of recurrence and to manage any ongoing symptoms or side effects.

